localhost
GET
¥Validation
创建 API 服务器的目的是获取输入并进行处理。
¥The purpose of creating an API server is to take an input and process it.
JavaScript 允许任何数据类型。Elysia 提供了一个开箱即用的数据验证工具,以确保数据格式正确。
¥JavaScript allows any data to be of any type. Elysia provides a tool to validate data out of the box to ensure that the data is in the correct format.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
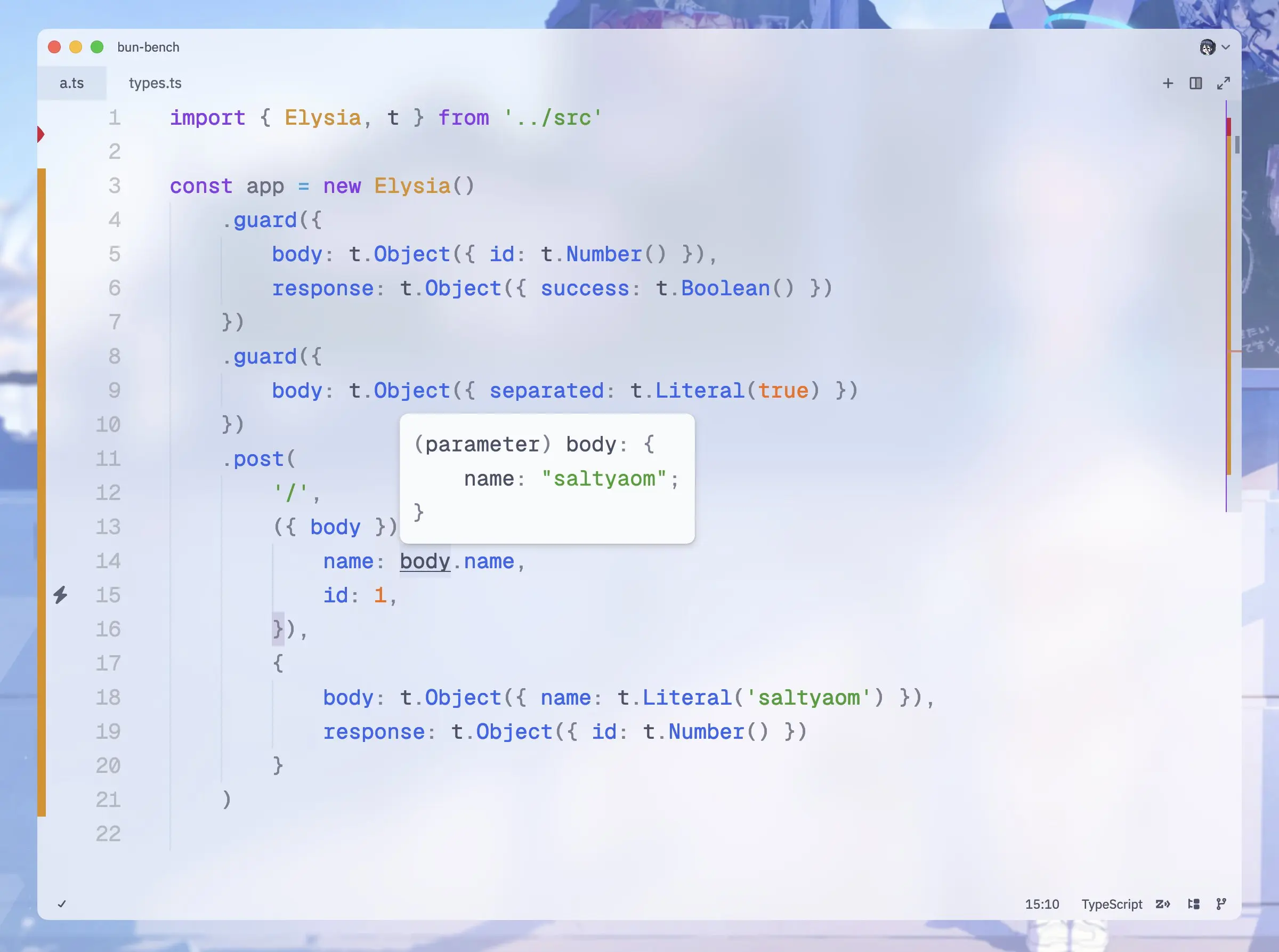
.get('/id/:id', ({ params: { id } }) => id, {
params: t.Object({
id: t.Number()
})
})
.listen(3000)Elysia.t 是一个基于 TypeBox 的模式构建器,它在运行时、编译时以及 OpenAPI 模式中提供类型安全,从而支持生成 OpenAPI 文档。
¥Elysia.t is a schema builder based on TypeBox that provides type-safety at runtime, compile-time, and for OpenAPI schemas, enabling the generation of OpenAPI documentation.
TypeBox 是一个非常快速、轻量级且类型安全的 TypeScript 运行时验证库。Elysia 扩展并自定义了 TypeBox 的默认行为,以满足服务器端验证的要求。
¥TypeBox is a very fast, lightweight, and type-safe runtime validation library for TypeScript. Elysia extends and customizes the default behavior of TypeBox to match server-side validation requirements.
我们相信验证至少应该由框架原生处理,而不是依赖用户为每个项目设置自定义类型。
¥We believe that validation should at least be handled by the framework natively, rather than relying on the user to set up a custom type for every project.
¥Standard Schema
Elysia 还支持 标准 Schema,允许你使用你最喜欢的验证库:
¥Elysia also support Standard Schema, allowing you to use your favorite validation library:
Zod
Valibot
ArkType
效果模式
是的
Joi
要使用标准模式,只需导入模式并将其提供给路由处理程序即可。
¥To use Standard Schema, simply import the schema and provide it to the route handler.
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
import { z } from 'zod'
import * as v from 'valibot'
new Elysia()
.get('/id/:id', ({ params: { id }, query: { name } }) => id, {
params: z.object({
id: z.coerce.number()
}),
query: v.object({
name: v.literal('Lilith')
})
})
.listen(3000)你可以在同一个处理程序中同时使用任何验证器,而不会出现任何问题。
¥You can use any validator together in the same handler without any issue.
我们可以通过访问 static 属性来获取每个 Elysia/TypeBox 类型的类型定义,如下所示:
¥We can get type definitions of every Elysia/TypeBox's type by accessing the static property as follows:
import { t } from 'elysia'
const MyType = t.Object({
hello: t.Literal('Elysia')
})
type MyType = typeof MyType.static
这允许 Elysia 自动推断并提供类型,从而减少声明重复模式的需要。
¥This allows Elysia to infer and provide type automatically, reducing the need to declare duplicate schema
单个 Elysia/TypeBox 模式可用于:
¥A single Elysia/TypeBox schema can be used for:
运行时验证
数据强制转换
TypeScript 类型
OpenAPI 架构
这使我们能够将模式作为单一事实来源。
¥This allows us to make a schema as a single source of truth.
¥Schema type
Elysia 支持以下类型的声明式模式:
¥Elysia supports declarative schemas with the following types:
这些属性应作为路由处理程序的第三个参数提供,以验证传入的请求。
¥These properties should be provided as the third argument of the route handler to validate the incoming request.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/id/:id', () => 'Hello World!', {
query: t.Object({
name: t.String()
}),
params: t.Object({
id: t.Number()
})
})
.listen(3000)GET
响应应如下所示:
¥The response should be as follows:
| URL | 查询 | 参数 |
|---|---|---|
| /id/a | ❌ | ❌ |
| /id/1?名称=Elysia | ✅ | ✅ |
| /id/1?别名=Elysia | ❌ | ✅ |
| /id/a?name=Elysia | ✅ | ❌ |
| /id/a?alias=Elysia | ❌ | ❌ |
当提供模式时,系统将自动从模式推断类型,并为 API 文档生成 OpenAPI 类型,从而省去了手动提供类型的冗余工作。
¥When a schema is provided, the type will be inferred from the schema automatically and an OpenAPI type will be generated for an API documentation, eliminating the redundant task of providing the type manually.
¥Guard
Guard 可用于将方案应用于多个处理程序。
¥Guard can be used to apply a schema to multiple handlers.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/none', ({ query }) => 'hi')
.guard({
query: t.Object({
name: t.String()
})
})
.get('/query', ({ query }) => query)
.listen(3000)此代码确保查询必须具有名称,并且其后的每个处理程序都必须具有字符串值。响应应如下所示:
¥This code ensures that the query must have name with a string value for every handler after it. The response should be listed as follows:
GET
响应应如下所示:
¥The response should be listed as follows:
| 路径 | 响应 |
|---|---|
| /none | hi |
| /none?name=a | hi |
| /query | error |
| /query?name=a | a |
如果为同一属性定义了多个全局模式,则最新的模式将优先。如果同时定义了本地模式和全局模式,则本地模式将优先。
¥If multiple global schemas are defined for the same property, the latest one will take precedence. If both local and global schemas are defined, the local one will take precedence.
¥Guard Schema Type
Guard 支持两种类型来定义验证。
¥Guard supports 2 types to define a validation.
¥override (default)
如果模式相互冲突,请覆盖模式。
¥Override schema if schema is collide with each others.
分离冲突的模式,并独立运行两者,从而对两者进行验证。
¥Separate collided schema, and runs both independently resulting in both being validated.

要使用 schema 定义 schema 类型的 guard:
¥To define schema type of guard with schema:
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.guard({
schema: 'standalone',
response: t.Object({
title: t.String()
})
})¥Body
传入的 HTTP 消息 是发送到服务器的数据。它可以采用 JSON、表单数据或任何其他格式。
¥An incoming HTTP Message is the data sent to the server. It can be in the form of JSON, form-data, or any other format.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.post('/body', ({ body }) => body, {
body: t.Object({
name: t.String()
})
})
.listen(3000)验证应如下所示:
¥The validation should be as follows:
| 正文 | 验证 |
|---|---|
| { name:'Elysia' } | ✅ |
| { name:1 } | ❌ |
| { alias:'Elysia' } | ❌ |
undefined | ❌ |
Elysia 默认禁用 GET 和 HEAD 消息的 body-parser,遵循 HTTP/1.1 RFC2616 规范。
¥Elysia disables body-parser for GET and HEAD messages by default, following the specs of HTTP/1.1 RFC2616
如果请求方法未包含实体主体的定义语义,则在处理请求时应忽略消息主体。
大多数浏览器默认禁用 GET 和 HEAD 方法的主体附件。
¥Most browsers disable the attachment of the body by default for GET and HEAD methods.
¥Specs
验证传入的 HTTP 消息(或主体)。
¥Validate an incoming HTTP Message (or body).
这些消息是 Web 服务器需要处理的附加消息。
¥These messages are additional messages for the web server to process.
主体的提供方式与 fetch API 中的 body 相同。内容类型应根据定义的主体进行设置。
¥The body is provided in the same way as the body in fetch API. The content type should be set accordingly to the defined body.
fetch('https://elysia.nodejs.cn', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({
name: 'Elysia'
})
})¥File
File 是一种特殊的主体类型,可用于上传文件。
¥File is a special type of body that can be used to upload files.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.post('/body', ({ body }) => body, {
body: t.Object({
file: t.File({ format: 'image/*' }),
multipleFiles: t.Files()
})
})
.listen(3000)通过提供文件类型,Elysia 将自动假定内容类型为 multipart/form-data。
¥By providing a file type, Elysia will automatically assume that the content-type is multipart/form-data.
¥File (Standard Schema)
如果你使用的是标准模式,请注意,Elysia 将无法像 t.File 一样自动验证内容类型。
¥If you're using Standard Schema, it's important that Elysia will not be able to valiate content type automatically similar to t.File.
但是 Elysia 导出了一个 fileType,可以使用魔法数字来验证文件类型。
¥But Elysia export a fileType that can be used to validate file type by using magic number.
import { Elysia, fileType } from 'elysia'
import { z } from 'zod'
new Elysia()
.post('/body', ({ body }) => body, {
body: z.object({
file: z.file().refine((file) => fileType(file, 'image/jpeg'))
})
})使用 fileType 验证文件类型非常重要,因为大多数验证器实际上并不能正确验证文件类型,例如检查内容类型及其值,这可能会导致安全漏洞。
¥It's very important that you should use fileType to validate the file type as most validator doesn't actually validate the file correctly, like checking the content type the value of it which can lead to security vulnerability.
¥Query
查询是通过 URL 发送的数据。它可以采用 ?key=value 的形式。
¥Query is the data sent through the URL. It can be in the form of ?key=value.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/query', ({ query }) => query, {
query: t.Object({
name: t.String()
})
})
.listen(3000)查询必须以对象的形式提供。
¥Query must be provided in the form of an object.
验证应如下所示:
¥The validation should be as follows:
| 查询 | 验证 |
|---|---|
| /?name=Elysia | ✅ |
| /?name=1 | ✅ |
| /?alias=Elysia | ❌ |
| /?name=ElysiaJS&alias=Elysia | ✅ |
| / | ❌ |
¥Specs
查询字符串是 URL 的一部分,以 ? 开头,可以包含一个或多个查询参数,这些参数是用于向服务器传递附加信息的键值对,通常用于自定义行为,例如过滤或搜索。
¥A query string is a part of the URL that starts with ? and can contain one or more query parameters, which are key-value pairs used to convey additional information to the server, usually for customized behavior like filtering or searching.
在 Fetch API 中,查询在 ? 之后提供。
¥Query is provided after the ? in Fetch API.
fetch('https://elysia.nodejs.cn/?name=Elysia')指定查询参数时,务必理解所有查询参数值都必须以字符串形式表示。这是由它们的编码方式以及附加到 URL 的方式决定的。
¥When specifying query parameters, it's crucial to understand that all query parameter values must be represented as strings. This is due to how they are encoded and appended to the URL.
¥Coercion
Elysia 将自动将 query 上适用的模式强制转换为相应的类型。
¥Elysia will coerce applicable schema on query to respective type automatically.
有关更多信息,请参阅 Elysia 行为。
¥See Elysia behavior for more information.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/', ({ query }) => query, {
query: t.Object({
name: t.Number()
})
})
.listen(3000)GET
¥Array
默认情况下,Elysia 将查询参数视为单个字符串,即使多次指定也是如此。
¥By default, Elysia treat query parameters as a single string even if specified multiple time.
要使用数组,我们需要将其明确声明为数组。
¥To use array, we need to explicitly declare it as an array.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/', ({ query }) => query, {
query: t.Object({
name: t.Array(t.String())
})
})
.listen(3000)GET
一旦 Elysia 检测到某个属性可以赋值给数组,Elysia 就会将其强制转换为指定类型的数组。
¥Once Elysia detect that a property is assignable to array, Elysia will coerce it to an array of the specified type.
默认情况下,Elysia 使用以下格式格式化查询数组:
¥By default, Elysia format query array with the following format:
此格式由 nuqs 使用。
¥This format is used by nuqs.
通过使用 , 作为分隔符,属性将被视为数组。
¥By using , as a delimiter, a property will be treated as array.
http://localhost?name=rapi,anis,neon&squad=counter
{
name: ['rapi', 'anis', 'neon'],
squad: 'counter'
}¥HTML form format
如果一个键被多次赋值,该键将被视为数组。
¥If a key is assigned multiple time, the key will be treated as an array.
这类似于 HTML 表单格式,当多次指定同名输入时。
¥This is similar to HTML form format when an input with the same name is specified multiple times.
http://localhost?name=rapi&name=anis&name=neon&squad=counter
// name: ['rapi', 'anis', 'neon']¥Params
参数或路径参数是通过 URL 路径发送的数据。
¥Params or path parameters are the data sent through the URL path.
它们可以采用 /key 的形式。
¥They can be in the form of /key.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/id/:id', ({ params }) => params, {
params: t.Object({
id: t.Number()
})
})GET
参数必须以对象的形式提供。
¥Params must be provided in the form of an object.
验证应如下所示:
¥The validation should be as follows:
| URL | 验证 |
|---|---|
| /id/1 | ✅ |
| /id/a | ❌ |
¥Specs
路径参数 (不要与查询字符串或查询参数混淆)。
¥Path parameter (not to be confused with query string or query parameter).
通常不需要此字段,因为 Elysia 可以自动从路径参数推断类型,除非需要特定的值模式,例如数值或模板字面量模式。
¥This field is usually not needed as Elysia can infer types from path parameters automatically, unless there is a need for a specific value pattern, such as a numeric value or template literal pattern.
fetch('https://elysia.nodejs.cn/id/1')¥Params type inference
如果没有提供 params 模式,Elysia 会自动将其类型推断为字符串。
¥If a params schema is not provided, Elysia will automatically infer the type as a string.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/id/:id', ({ params }) => params)
¥Headers
Headers 是通过请求标头发送的数据。
¥Headers are the data sent through the request's header.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/headers', ({ headers }) => headers, {
headers: t.Object({
authorization: t.String()
})
})与其他类型不同,Headers 默认将 additionalProperties 设置为 true。
¥Unlike other types, headers have additionalProperties set to true by default.
这意味着 headers 可以包含任何键值对,但值必须与 schema 匹配。
¥This means that headers can have any key-value pair, but the value must match the schema.
¥Specs
HTTP 标头允许客户端和服务器通过 HTTP 请求或响应传递附加信息,通常被视为元数据。
¥HTTP headers let the client and the server pass additional information with an HTTP request or response, usually treated as metadata.
此字段通常用于强制某些特定的标头字段,例如 Authorization。
¥This field is usually used to enforce some specific header fields, for example, Authorization.
标头的提供方式与 fetch API 中的 body 相同。
¥Headers are provided in the same way as the body in fetch API.
fetch('https://elysia.nodejs.cn/', {
headers: {
authorization: 'Bearer 12345'
}
})提示
Elysia 将仅将标头解析为小写键。
¥Elysia will parse headers as lower-case keys only.
请确保使用标头验证时字段名称小写。
¥Please make sure that you are using lower-case field names when using header validation.
Cookie 是通过请求的 Cookie 发送的数据。
¥Cookie is the data sent through the request's cookie.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/cookie', ({ cookie }) => cookie, {
cookie: t.Cookie({
cookieName: t.String()
})
})Cookie 必须以 t.Cookie 或 t.Object 的形式提供。
¥Cookies must be provided in the form of t.Cookie or t.Object.
与 headers 相同,cookie 默认将 additionalProperties 设置为 true。
¥Same as headers, cookies have additionalProperties set to true by default.
¥Specs
HTTP Cookie 是服务器发送给客户端的一小段数据。它是每次访问同一 Web 服务器时发送的数据,以便服务器记住客户端信息。
¥An HTTP cookie is a small piece of data that a server sends to the client. It's data that is sent with every visit to the same web server to let the server remember client information.
简而言之,它是随每个请求发送的字符串化状态。
¥In simpler terms, it's a stringified state that is sent with every request.
此字段通常用于强制某些特定的 Cookie 字段。
¥This field is usually used to enforce some specific cookie fields.
Cookie 是一个特殊的标头字段,Fetch API 不接受自定义值,而是由浏览器管理。要发送 Cookie,你必须改用 credentials 字段:
¥A cookie is a special header field that the Fetch API doesn't accept a custom value for but is managed by the browser. To send a cookie, you must use a credentials field instead:
fetch('https://elysia.nodejs.cn/', {
credentials: 'include'
})t.Cookie 是一种特殊类型,相当于 t.Object,但允许设置特定于 cookie 的选项。
¥t.Cookie is a special type that is equivalent to t.Object but allows to set cookie-specific options.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/cookie', ({ cookie }) => cookie.name.value, {
cookie: t.Cookie({
name: t.String()
}, {
secure: true,
httpOnly: true
})
})¥Response
响应是从处理程序返回的数据。
¥Response is the data returned from the handler.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/response', () => {
return {
name: 'Jane Doe'
}
}, {
response: t.Object({
name: t.String()
})
})¥Response per status
可以根据状态码设置响应。
¥Responses can be set per status code.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.get('/response', ({ status }) => {
if (Math.random() > 0.5)
return status(400, {
error: 'Something went wrong'
})
return {
name: 'Jane Doe'
}
}, {
response: {
200: t.Object({
name: t.String()
}),
400: t.Object({
error: t.String()
})
}
})这是 Elysia 特有的功能,允许我们将字段设为可选。
¥This is an Elysia-specific feature, allowing us to make a field optional.
¥Error Provider
验证失败时,有两种方法可以自定义错误消息:
¥There are two ways to provide a custom error message when the validation fails:
status 属性¥Error Property
Elysia 提供了一个额外的错误属性,允许我们在字段无效时返回自定义错误消息。
¥Elysia offers an additional error property, allowing us to return a custom error message if the field is invalid.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.post('/', () => 'Hello World!', {
body: t.Object({
x: t.Number({
error: 'x must be a number'
})
})
})
.listen(3000)以下是在各种类型上使用 error 属性的示例:
¥The following is an example of using the error property on various types:
| TypeBox | Error |
typescript | |
typescript | |
typescript | |
typescript | |
¥Custom Error
TypeBox 提供了一个额外的 "error" 属性,允许我们在字段无效时返回自定义错误消息。
¥TypeBox offers an additional "error" property, allowing us to return a custom error message if the field is invalid.
| TypeBox | Error |
typescript | |
typescript | |
¥Error message as function
除了字符串之外,Elysia 类型的错误还可以接受一个函数,以编程方式为每个属性返回自定义错误。
¥In addition to a string, Elysia type's error can also accept a function to programmatically return a custom error for each property.
错误函数接受与 ValidationError 相同的参数
¥The error function accepts the same arguments as ValidationError
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.post('/', () => 'Hello World!', {
body: t.Object({
x: t.Number({
error() {
return 'Expected x to be a number'
}
})
})
})
.listen(3000)提示
将鼠标悬停在 error 上即可查看类型。
¥Hover over the error to see the type.
¥Error is Called Per Field
请注意,只有字段无效时才会调用错误函数。
¥Please note that the error function will only be called if the field is invalid.
请参考下表:
¥Please consider the following table:
| Code | Body | Error |
typescript | json | Expected x to be a number |
typescript | json | (default error, `t.Number.error` is not called) |
typescript | json | Expected value to be an object |
我们可以通过将错误代码缩小到 "VALIDATION" 来自定义基于 onError 事件的验证行为。
¥We can customize the behavior of validation based on the onError event by narrowing down the error code to "VALIDATION".
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.onError(({ code, error }) => {
if (code === 'VALIDATION')
return error.message
})
.listen(3000)从 elysia/error 导入后,缩小的错误类型将被定义为 ValidationError。
¥The narrowed-down error type will be typed as ValidationError imported from elysia/error.
ValidationError 公开一个名为 validator 的属性,类型为 TypeCheck,允许我们开箱即用地与 TypeBox 功能进行交互。
¥ValidationError exposes a property named validator, typed as TypeCheck, allowing us to interact with TypeBox functionality out of the box.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.onError(({ code, error }) => {
if (code === 'VALIDATION')
return error.all[0].message
})
.listen(3000)¥Error List
ValidationError 提供了一个方法 ValidatorError.all,允许我们列出所有错误原因。
¥ValidationError provides a method ValidatorError.all, allowing us to list all of the error causes.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
new Elysia()
.post('/', ({ body }) => body, {
body: t.Object({
name: t.String(),
age: t.Number()
}),
error({ code, error }) {
switch (code) {
case 'VALIDATION':
console.log(error.all)
// Find a specific error name (path is OpenAPI Schema compliance)
const name = error.all.find(
(x) => x.summary && x.path === '/name'
)
// If there is a validation error, then log it
if(name)
console.log(name)
}
}
})
.listen(3000)有关 TypeBox 验证器的更多信息,请参阅 TypeCheck。
¥For more information about TypeBox's validator, see TypeCheck.
¥Reference Model
有时你可能会发现自己声明了重复的模型或多次重复使用同一个模型。
¥Sometimes you might find yourself declaring duplicate models or re-using the same model multiple times.
通过引用模型,我们可以命名模型并通过引用名称来重用它。
¥With a reference model, we can name our model and reuse it by referencing the name.
让我们从一个简单的场景开始。
¥Let's start with a simple scenario.
假设我们有一个使用相同模型处理登录的控制器。
¥Suppose we have a controller that handles sign-in with the same model.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
.post('/sign-in', ({ body }) => body, {
body: t.Object({
username: t.String(),
password: t.String()
}),
response: t.Object({
username: t.String(),
password: t.String()
})
})我们可以通过将模型提取为变量并引用它来重构代码。
¥We can refactor the code by extracting the model as a variable and referencing it.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
// Maybe in a different file eg. models.ts
const SignDTO = t.Object({
username: t.String(),
password: t.String()
})
const app = new Elysia()
.post('/sign-in', ({ body }) => body, {
body: SignDTO,
response: SignDTO
})这种分离关注点的方法是一种有效的方法,但随着应用变得越来越复杂,我们可能会发现自己需要重复使用具有不同控制器的多个模型。
¥This method of separating concerns is an effective approach, but we might find ourselves reusing multiple models with different controllers as the app gets more complex.
我们可以通过创建 "参考模型" 来解决这个问题,允许我们命名模型并使用自动补齐功能,通过将模型注册到 model,在 schema 中直接引用它。
¥We can resolve that by creating a "reference model", allowing us to name the model and use auto-completion to reference it directly in schema by registering the models with model.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
.model({
sign: t.Object({
username: t.String(),
password: t.String()
})
})
.post('/sign-in', ({ body }) => body, {
// with auto-completion for existing model name
body: 'sign',
response: 'sign'
})当我们想要访问模型组时,可以将 model 分离为一个插件,该插件注册后将提供一组模型,而不是多次导入。
¥When we want to access the model's group, we can separate a model into a plugin, which when registered will provide a set of models instead of multiple imports.
// auth.model.ts
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
export const authModel = new Elysia()
.model({
sign: t.Object({
username: t.String(),
password: t.String()
})
})然后在实例文件中:
¥Then in an instance file:
// index.ts
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
import { authModel } from './auth.model'
const app = new Elysia()
.use(authModel)
.post('/sign-in', ({ body }) => body, {
// with auto-completion for existing model name
body: 'sign',
response: 'sign'
})这种方法不仅允许我们分离关注点,还使我们能够在将模型集成到 OpenAPI 文档中时在多个位置重用该模型。
¥This approach not only allows us to separate concerns but also enables us to reuse the model in multiple places while integrating the model into OpenAPI documentation.
¥Multiple Models
model 接受一个对象,其键作为模型名称,值作为模型定义。默认支持多个模型。
¥model accepts an object with the key as a model name and the value as the model definition. Multiple models are supported by default.
// auth.model.ts
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
export const authModel = new Elysia()
.model({
number: t.Number(),
sign: t.Object({
username: t.String(),
password: t.String()
})
})¥Naming Convention
重复的模型名称将导致 Elysia 抛出错误。为了防止声明重复的模型名称,我们可以使用以下命名约定。
¥Duplicate model names will cause Elysia to throw an error. To prevent declaring duplicate model names, we can use the following naming convention.
假设我们将所有模型存储在 models/<name>.ts 中,并将模型的前缀声明为命名空间。
¥Let's say that we have all models stored at models/<name>.ts and declare the prefix of the model as a namespace.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
// admin.model.ts
export const adminModels = new Elysia()
.model({
'admin.auth': t.Object({
username: t.String(),
password: t.String()
})
})
// user.model.ts
export const userModels = new Elysia()
.model({
'user.auth': t.Object({
username: t.String(),
password: t.String()
})
})这可以在一定程度上防止命名重复,但最终最好让你的团队自行决定命名约定。
¥This can prevent naming duplication to some extent, but ultimately, it's best to let your team decide on the naming convention.
Elysia 提供了一个灵活的选项,有助于避免决策疲劳。
¥Elysia provides an opinionated option to help prevent decision fatigue.